I use Virt-Manager (Virtual Machine Manager GUI for libvirt) to easily manage virtual machine on my personal laptop. It’s easy and works great for “normal use” of KVM/QEMU. But, you may need to do little extra steps to be able to share data between host and multiple Linux guests.
Although it is possible to use network file systems such as NFS/CIFS for some of these tasks, they require configuration steps that are hard to automate, maintain, monitor, and you need to expose the storage network to the guests.
The easiest way (at least for me) to solve these problems without configuring network file systems is using virtio-fs. It also takes advantage of the co-location of the guest and host to increase performance and provide semantics that are not possible with network file systems.
Before going any further, let’s take a look to my laptop disks allocation:
1df -h | grep '/dev/sd'
2/dev/sda3 442G 164G 256G 40% /
3/dev/sdc1 469G 66G 380G 15% /mnt/msata
4/dev/sda1 511M 144K 511M 1% /efi
5/dev/sdb1 916G 588G 282G 68% /mnt/hdd2
/dev/sda500GB SATA SSD (main host operating system)./dev/sdb11TB SATA HDD mounted to/mnt/hdd2(which I want to share that path to Linux guests)./dev/sdc1500GB mSATA SSD mounted to/mnt/msata(which I place all the VMs disks).
Setting up guest VMs
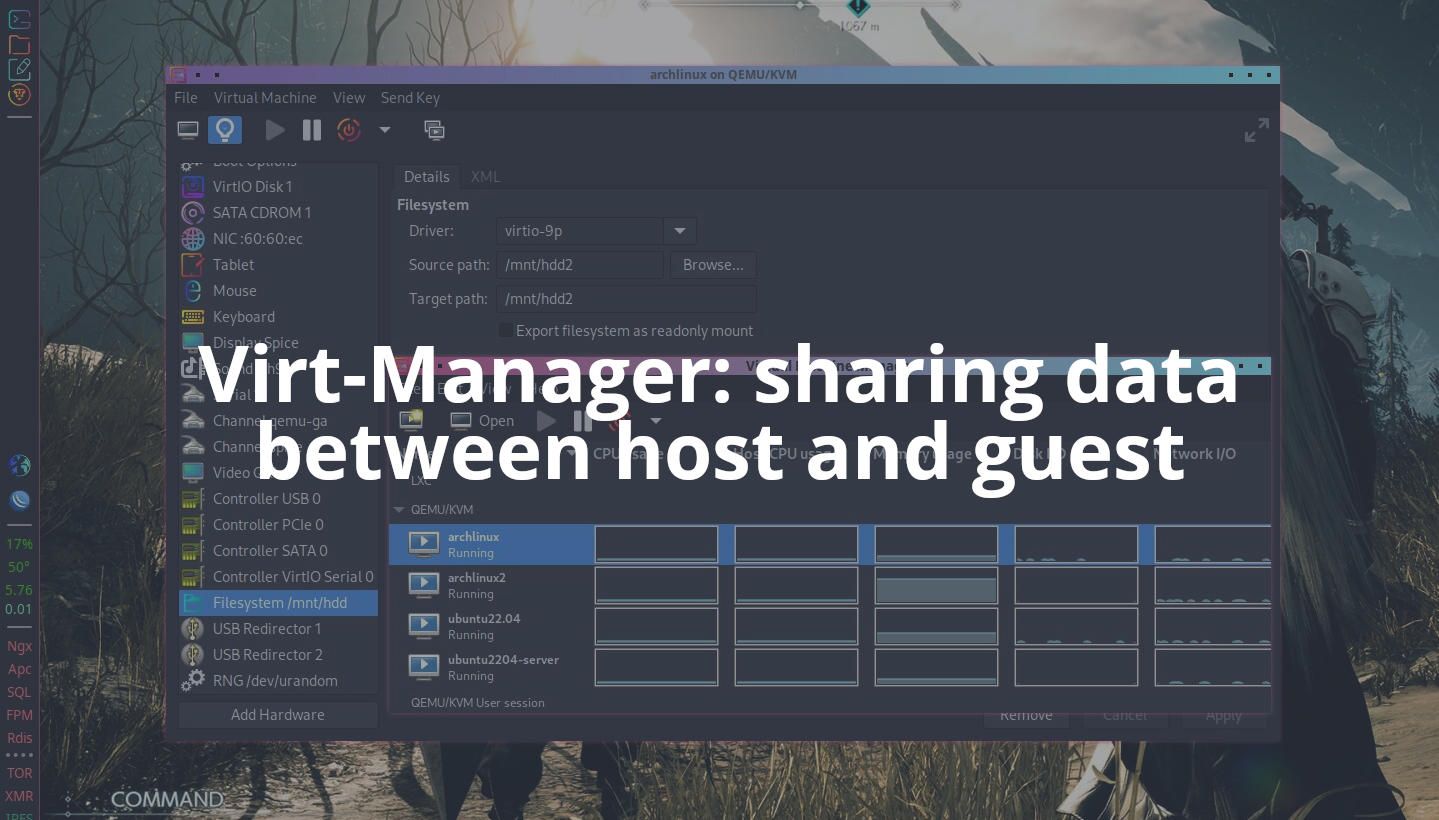
Open Virt-Manager → choose VM(s) → Add Hardware → Filesystem.
Choose virtio-9p for Driver, /path/to/mount_point/on/guest for Source path, and /mnt/hdd2 for Target path.
Target path is the path where the share folder you want to share on Host machine, and Source path is the path where you mount the shared folder on Guest(s) machine.
Login to your guest VM(s), install qemu-guest-agent and virtio-fs driver.
For Debian based distros:
1apt install qemu-guest-agent guestfsd
For Arch based distros:
1pacman -S qemu-guest-agent qemu-virtiofsd
Mount the virtio-fs as root user:
1mount -t 9p -o trans=virtio,version=9p2000.L /mnt/hdd2 /path/to/mount_point/on/guest
Mount at boot using /etc/fstab
You may want to auto-mount the file system when the VM boots. The kernel module for the 9p transport will not be automatically loaded, so mounting the file system from /etc/fstab will fail and you will encounter an error.
The solution is to preload the module during boot by creating /etc/modules-load.d/9pnet_virtio.conf file and fill with 9pnet_virtio module.
1echo 9pnet_virtio > /etc/modules-load.d/9pnet_virtio.conf